A chronic or persistent urinary tract infection is an ongoing infection of the urinary tract for a prolonged period despite treatment.
The infection may recur if the urinary tract gets re-infected or the treatment does not clear the infection completely.
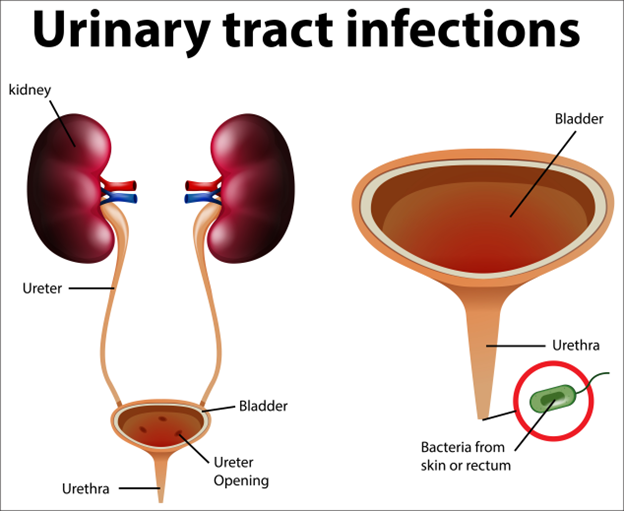
Urinary Tract Infections can affect any part of the urinary system, from the kidney to the bladder to ureters (tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder) or urethra (the tube that carries urine from the bladder to outside the body).
The severity of the infection depends on the part of the urinary system affected (bladder infections can be minor and treated easily, whereas infection spread to kidneys may lead to serious health consequences and may even need hospitalization).
Symptoms of Chronic Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
UTI symptoms include:
- Frequent peeing
- Feeling the need to pee even after emptying the bladder
- Burning sensation while peeing
- Bloody or dark urine
- Pain in the lower back or below the ribs (kidneys)
- Pain in the abdomen (bladder region)
- Nausea & vomiting
- Chills and high fever
- Fatigue
Causes and Risk Factors of Chronic Urinary Infection (UTI)
It is essential to identify the underlying UTI causes and risk factors to prevent recurrent infections and potential complications which include:
- Gender (more in females)
- History of kidney stones
- Weakened immune system
- Being pregnant
- Having unsafe sex
- Prior history of UTI
- Using a diaphragm during sex
- Using oral contraceptives and spermicides
- Hormonal changes during menopause
- Genetic factors
- Infections
- Urinary tract abnormalities
- Enlarged prostate
Chronic Urinary Tract Infection Treatment (UTI)
- Medications (Antibiotics for UTI) are the first line of treatment for urine infection
- Pain-relieving medications to ease discomfort
- Home remedies like drinking plenty of water, cranberry juice, etc.
What Are the Complications of Having Chronic Urinary Tract Infection?
An untreated UTI can lead to a kidney infection. A kidney infection may further lead to permanent kidney damage if left untreated.
Chronic UTIs, if left untreated, cause sepsis (blood poisoning) which can be life-threatening.
How To Prevent Chronic Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)?
Prevention of UTI is possible with the following:
- Drink plenty of water
- Urinate as often as needed
- Wipe from front to back
- Drink cranberry juice often
- Avoid tight-fitting pants
- Avoid diaphragms and spermicides for birth control
- Use lubrication during sex, if necessary
- Avoid bubble baths
- Avoid fluids that irritate the bladder (like coffee, citrus fruit drinks, soda, and alcohol)
- Wash your foreskin regularly if you are uncircumcised
Frequently Asked Questions
Will a urinary tract infection go away on its own?
Some less complicated UTIs can resolve without treatment. However, it would help if you saw a doctor to relieve symptoms associated with UTI. Untreated UTI can progress into kidney infection.
Why are women at a higher risk of getting Chronic UTIs?
Chronic UTIs are most common in women. This is due to two different aspects:
- The urethra (the tube that carries urine from the bladder to outside the body) is close to the rectum in females compared to males, which makes it extremely easy for the bacteria (from the rectum) to reach the urethra.
- The urethra is shorter in women (compared to men), so there is a shorter distance for the bacteria to travel to the bladder, where they can multiply and cause infection.
Did You Know?
- The bacteria that cause a UTI can come from your skin or rectum.
- The UTI can occur anywhere in your urinary tract, including your kidneys, bladder, or urethra.
- Women are more likely than men to get UTIs. Around 36% of younger women and 53% of women above the age of 55 years report a recurrence within one year
In conclusion, chronic UTIs can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. It is important to recognize the symptoms, seek proper diagnosis and treatment, and take preventative measures to reduce the risk of future infections.